How does Calibration Professionals Ensure Measurement Confidence Across Industries?
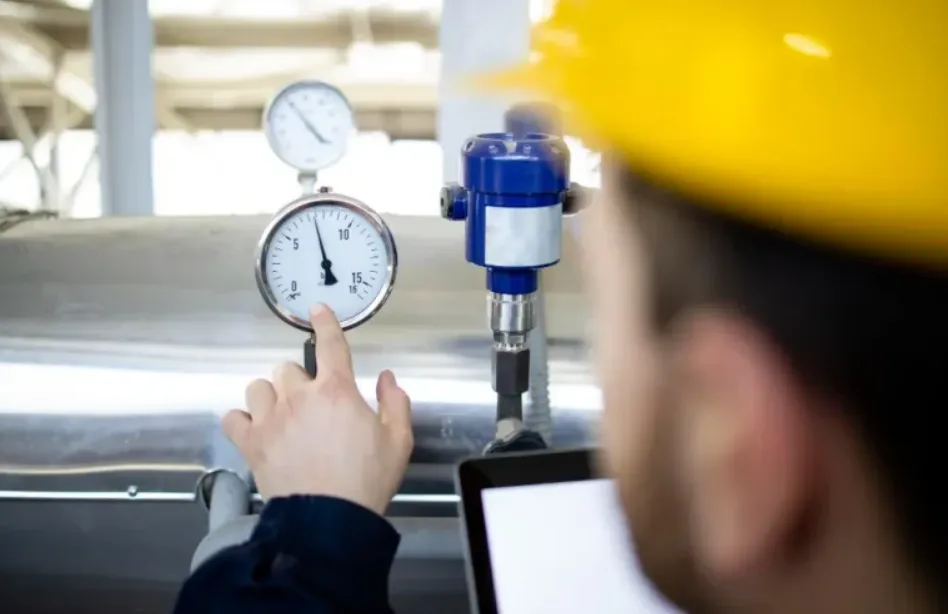

Accurate measurement is central to modern industry, science, and technology. From manufacturing lines and laboratories to environmental monitoring and healthcare devices, dependable readings influence safety, quality, and decision-making. Calibration professionals support this accuracy by ensuring instruments report values that align with accepted standards. Their work often goes unnoticed because it happens quietly in controlled settings, yet its impact reaches far beyond the calibration bench. Understanding how calibration professionals operate helps clarify why consistent measurement confidence is essential for reliable outcomes. Their role is not limited to adjustments; it also includes evaluation, documentation, and ensuring long-term consistency across systems that depend on precise data.
How calibration supports dependable measurements
- Establishing Measurement Baselines and Traceability
Calibration begins by establishing clear baselines against which instruments can be compared. Professionals rely on traceable references that link measurements back to recognized standards. This traceability ensures that readings taken today remain comparable to readings taken months or years later. Without consistent baselines, data loses meaning across time and locations. Calibration professionals carefully assess instrument condition before any adjustment, observing how readings deviate under known conditions. In environments supported by calibration experts at Allometrics Inc, this process emphasizes consistency rather than quick correction. Establishing traceability provides confidence that measurements remain aligned with broader systems, allowing organizations to trust the data they collect and use.
- Evaluating Instrument Behavior Over Time
Instruments rarely drift suddenly; changes usually occur gradually as components age or environmental conditions shift. Calibration professionals evaluate how instruments perform over time rather than focusing solely on a single point in time. By reviewing historical performance data, they identify patterns that indicate predictable drift or instability. This evaluation helps determine appropriate calibration intervals and supports proactive planning. Understanding long-term behavior enables adjustments with minimal disruption to operations. Rather than reacting to failure, calibration professionals support steady performance through observation and trend analysis. This approach protects measurement reliability while reducing unexpected downtime.
- A Brief Perspective on Measurement Confidence
Measurement confidence is built through repetition and consistency. When instruments deliver consistent, reliable results, users trust the data without hesitation. Calibration supports this trust by reinforcing alignment with standards. Confidence grows not from a single adjustment, but from ongoing verification. Reliable measurement becomes part of daily operations rather than a recurring concern.
- Environmental Influence on Measurement Accuracy
Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and vibration influence measurement accuracy more than many realize. Calibration professionals account for these factors when evaluating instruments. A device calibrated in one environment may behave differently in another if conditions vary significantly. By accounting for environmental factors, calibration professionals ensure that adjustments remain valid under actual operating conditions. This awareness supports accuracy beyond the controlled calibration setting. Addressing environmental effects helps prevent false confidence in readings that may shift when instruments are returned to active use. Understanding these influences reinforces the importance of context in measurement reliability.
- Documentation and Data Integrity
Documentation plays a central role in calibration work. Calibration professionals meticulously record procedures, reference values, measurement results, and adjustment outcomes. These records provide transparency and support audits, quality systems, and regulatory requirements. Accurate documentation ensures that calibration history is preserved and accessible. Data integrity depends on clear records that reflect what was done and why. When documentation is thorough, it supports informed decisions about maintenance, replacement, or recalibration. This written trail reinforces accountability and helps organizations demonstrate the reliability of measurement over time.
- Supporting Quality Systems and Compliance
Calibration professionals contribute directly to quality systems by ensuring instruments meet defined performance criteria. Many industries rely on calibration records to demonstrate compliance with internal standards and external regulations. By maintaining measurement accuracy, calibration supports product consistency and safety. Professionals work within established frameworks that emphasize repeatability and verification. Their role helps organizations align operational practices with quality expectations. This alignment supports confidence among stakeholders who rely on consistent measurement outcomes to assess performance and risk.
- Managing Calibration Intervals Strategically
Determining how often instruments require calibration is not arbitrary. Calibration professionals consider usage frequency, environmental exposure, historical drift, and measurement criticality. Strategic interval management balances reliability with efficiency. Calibrating too frequently may disrupt operations, while calibrating too infrequently increases risk. Professionals evaluate these factors to recommend intervals that support stability. This thoughtful approach ensures that calibration efforts align with actual needs rather than fixed assumptions. Interval management becomes part of a broader strategy for sustaining dependable measurements.
- Communication Between Technical Teams
Calibration professionals often act as a bridge between technical teams and operational staff. Clear communication ensures that instrument limitations and requirements are understood. When users know how instruments behave and what calibration supports, they can interpret data more effectively. Communication also helps identify issues early, such as unusual readings or environmental changes. This collaboration supports shared responsibility for measurement reliability. By fostering understanding across teams, calibration professionals help ensure accuracy is integrated into daily workflows.
- Adapting to Advancing Measurement Technology
Measurement technology continues to evolve, introducing digital systems, automation, and remote monitoring. Calibration professionals adapt their practices to align with these advancements. While tools change, the underlying principles of accuracy, traceability, and consistency remain constant. Professionals evaluate new technologies to ensure they meet reliability expectations. This adaptability keeps calibration practices relevant while supporting innovation. Embracing new methods without compromising measurement confidence is a key part of the calibration role.
- Long-Term Impact on Decision-Making
Reliable measurements influence decisions across operations, research, and safety planning. Calibration professionals support this reliability by ensuring data reflects reality as closely as possible. When measurements are dependable, decisions are based on solid foundations rather than uncertainty. Over time, this reliability reduces risk and improves outcomes. Calibration work quietly supports confidence in every downstream data-driven decision.
Calibration professionals play an essential role in maintaining measurement confidence across industries. Through traceability, environmental awareness, documentation, and strategic planning, they ensure instruments deliver reliable data over time. Their work supports quality systems, compliance, and informed decision-making without drawing attention to itself. Understanding the role of calibration professionals highlights why accurate measurement is not accidental but the result of ongoing care and evaluation. When calibration is approached thoughtfully, it becomes a foundation for trust in the data that shapes modern operations and innovation.